Greenhouse
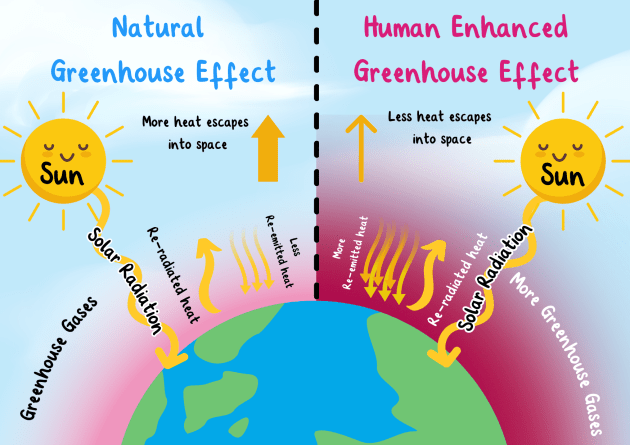
The greenhouse effect is a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface. When the sun’s energy reaches the Earth, some of it is reflected back to space, while the rest is absorbed and re-radiated as heat. This heat is trapped by greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and water vapor (H2O). This trapped heat keeps the Earth’s temperature stable enough to support life.
How the Greenhouse Effect Works
The sun emits energy in the form of light and heat. When this energy reaches the Earth’s surface, it is absorbed and then radiated back into the atmosphere as infrared radiation (heat). This gases, which are present in the atmosphere in small amounts, absorb this infrared radiation and trap it, preventing it from escaping back into space. As a result, the atmosphere heats up, creating what is known as the greenhouse effect.
Importance of the Greenhouse Effect
Without This effect, the Earth’s average temperature would be much colder, about -18°C (0°F), making it impossible for most forms of life to survive. This effect is essential for maintaining the planet’s temperature within a range that supports ecosystems, weather patterns, and human activities.
As more this gases are added to the atmosphere, more heat is trapped, leading to global warming and climate change. This results in various environmental impacts, including:
- Rising global temperatures
- Melting polar ice caps and glaciers
- Rising sea levels
- More frequent and severe weather events (such as storms, droughts, and floods)
- Disruption of ecosystems and biodiversity
Mitigating the Problem
To address the enhanced greenhouse effect, global efforts focus on reducing greenhouse gas emissions. This can be achieved by:
- Switching to renewable energy sources (solar, wind, hydro)
- Improving energy efficiency
- Protecting forests that absorb CO2
- Promoting sustainable agriculture and land use
- Encouraging behavioral changes, such as reducing energy consumption and supporting eco-friendly practices
In conclusion, while the effect is a natural and necessary process for life on Earth, human activities are amplifying it, causing climate-related challenges. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is critical to mitigating these effects and protecting the environment for future generations.